Details
Part No: 04B-350
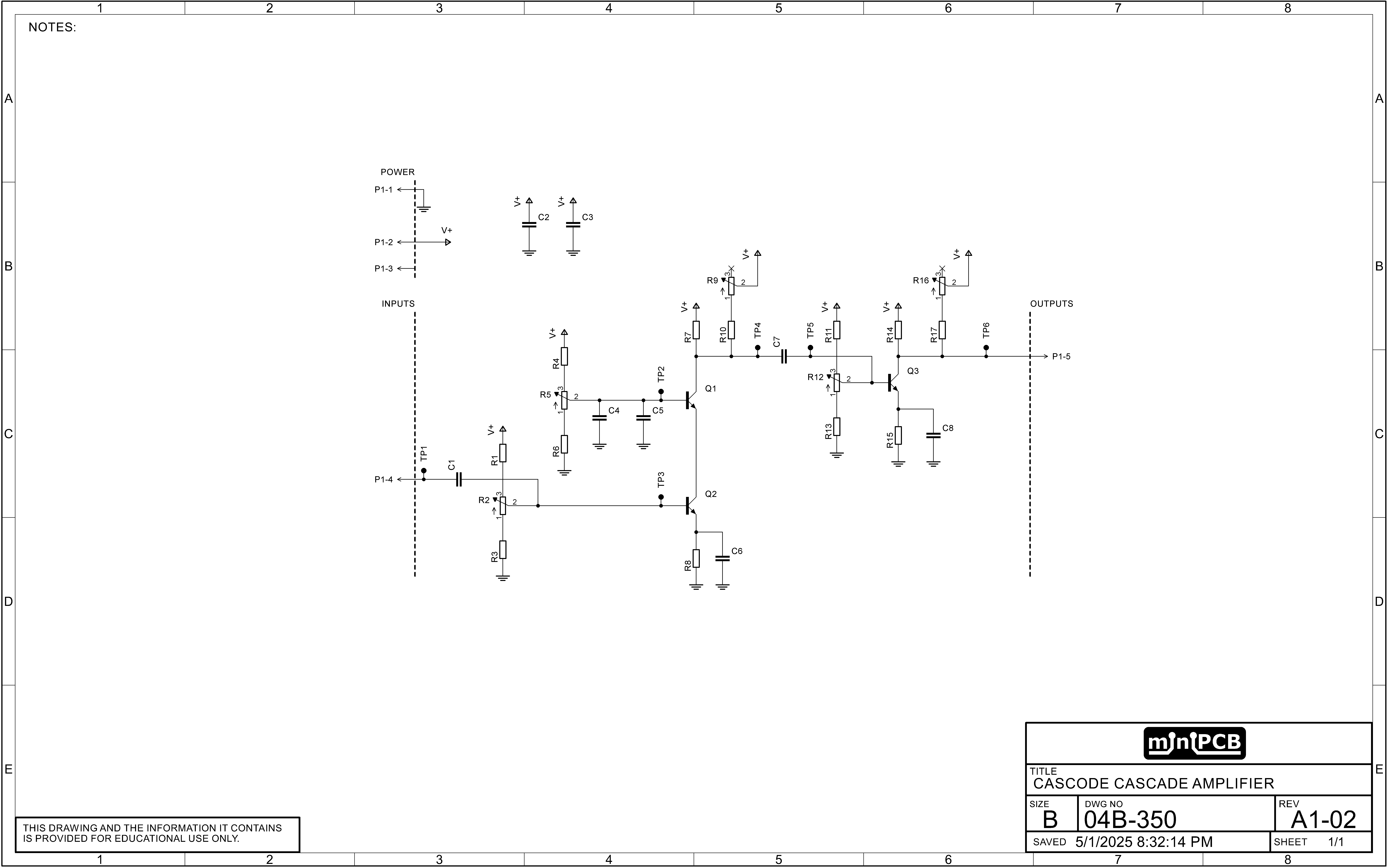
Title: Cascode Cascade Amplifier
Board Size: Approx. 75 x 50 mm
Pieces per Panel: 2
Panel Size: 75 x 100 mm (V-scored)
Description
AI Seed
AI Generated
Videos
Schematic
Layout
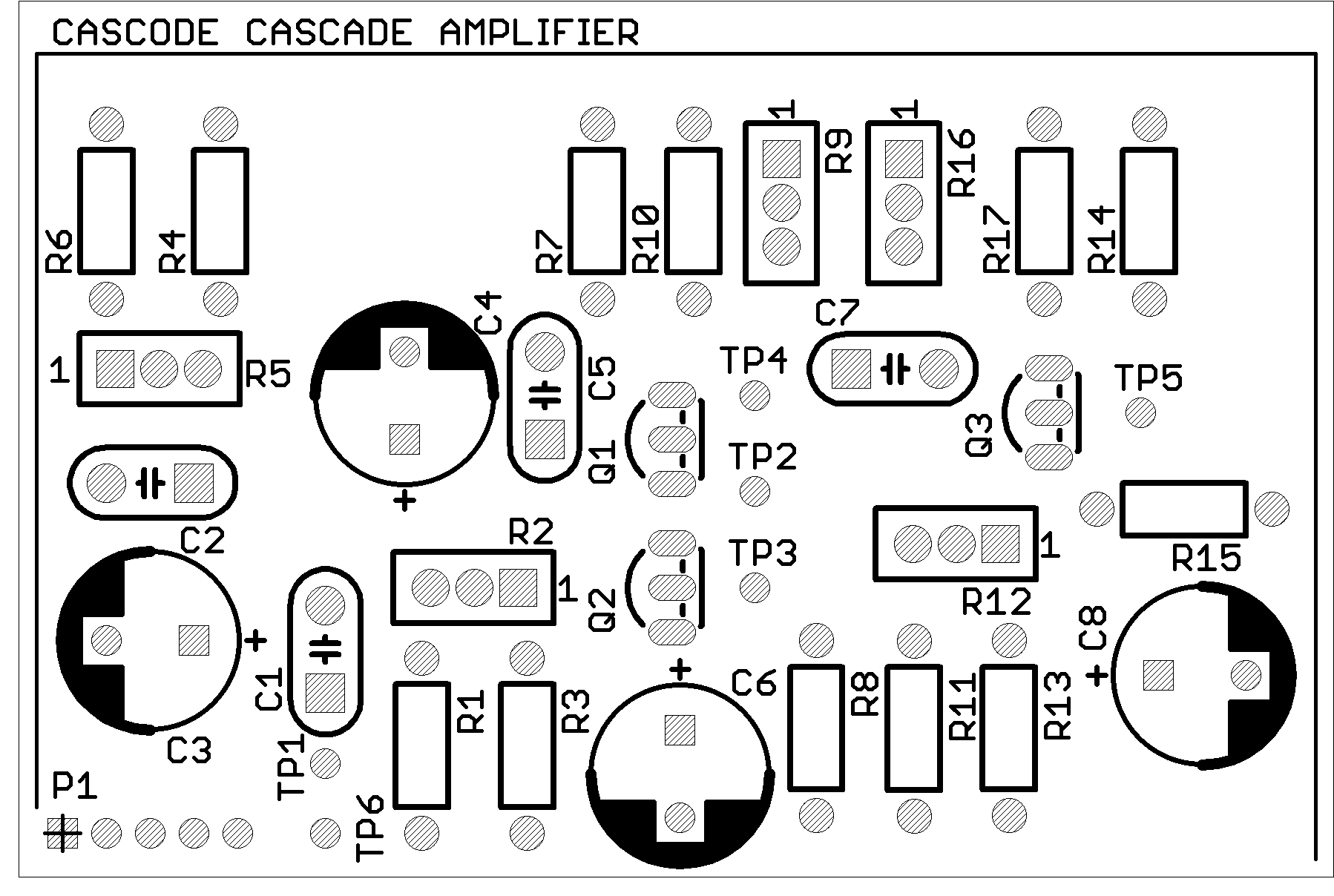
A foundational BJT amplifier for teaching gain, biasing, and small-signal response.
Part No: 04B-350
Title: Cascode Cascade Amplifier
Board Size: Approx. 75 x 50 mm
Pieces per Panel: 2
Panel Size: 75 x 100 mm (V-scored)

