Details
Part No: 04B-345
Title: Cascade Amplifier
Board Size: Approx. 75 x 50 mm
Pieces per Panel: 2
Panel Size: 75 x 100 mm (V-scored)
Description
AI Seed
AI Generated
Videos
Schematic
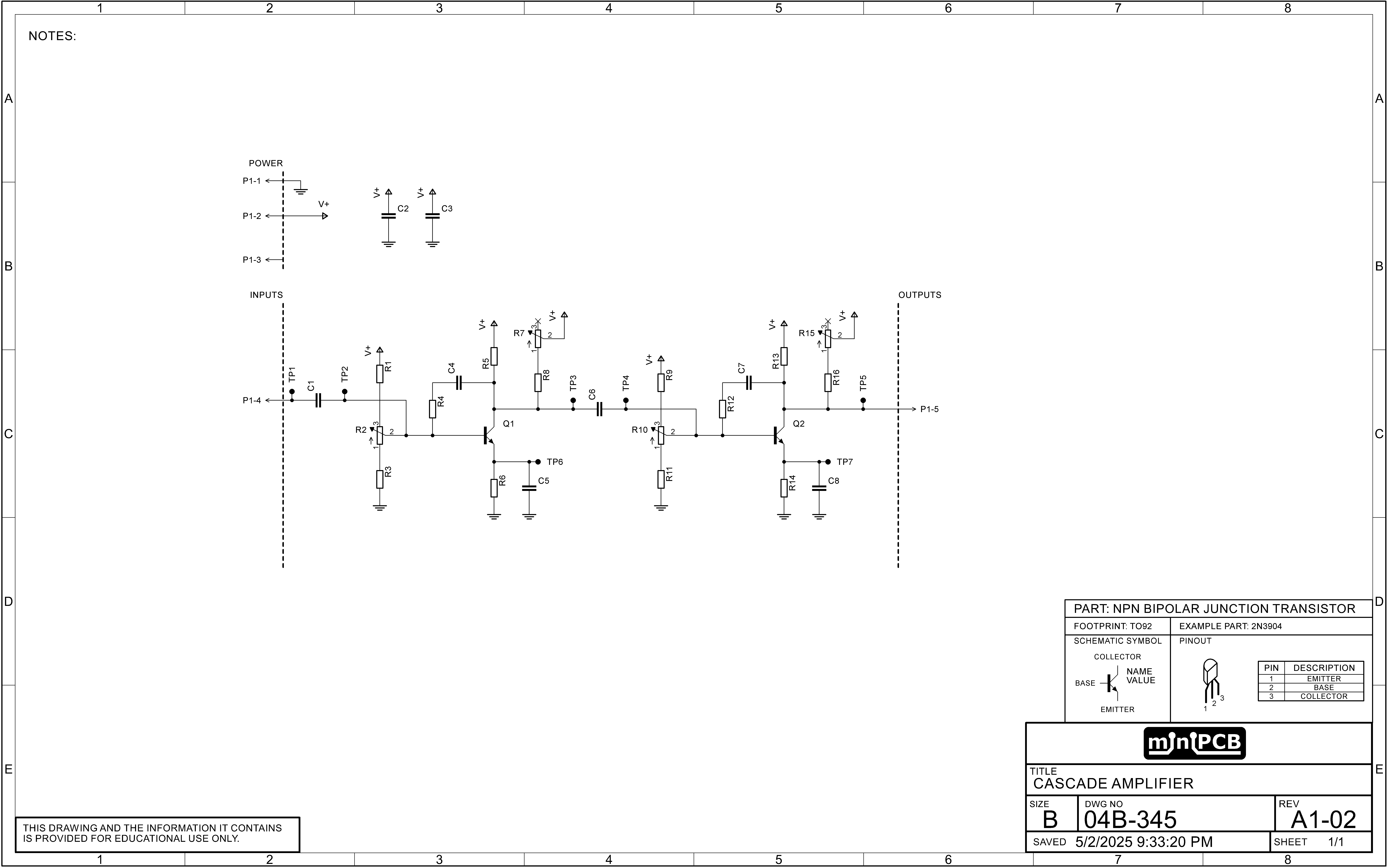
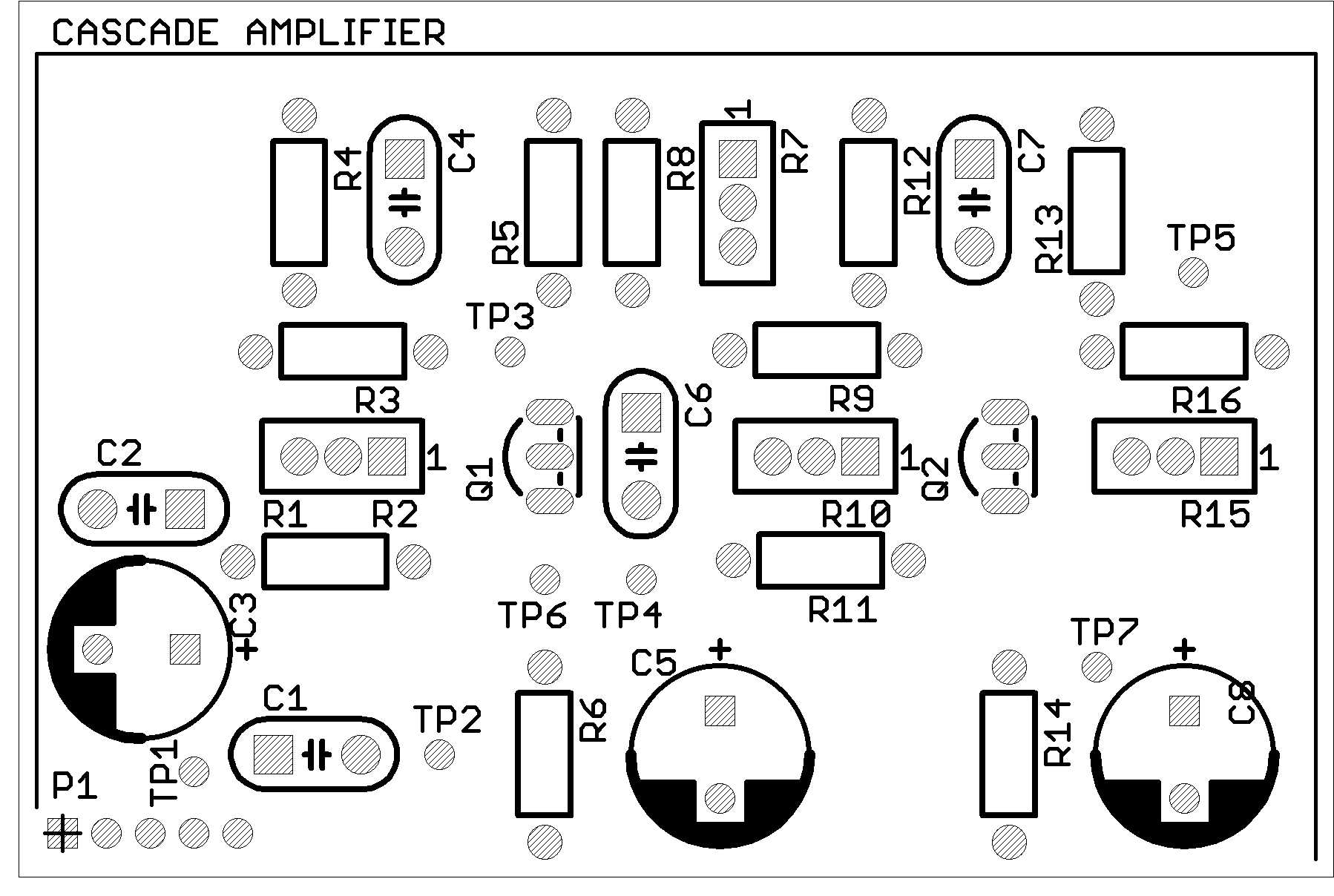
Layout
Downloads
Additional Resources
| Date | Revision | Description | By |
|---|